- February 12, 2024
- Posted by: CoachShane
- Categories: Options Trading, Trading Article

Vega measures the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the volatility of the underlying asset. A higher vega means the option’s price is more sensitive to volatility. For traders, this means that as market volatility increases, options with high vega could see more significant price movements, presenting potential opportunities or risks.
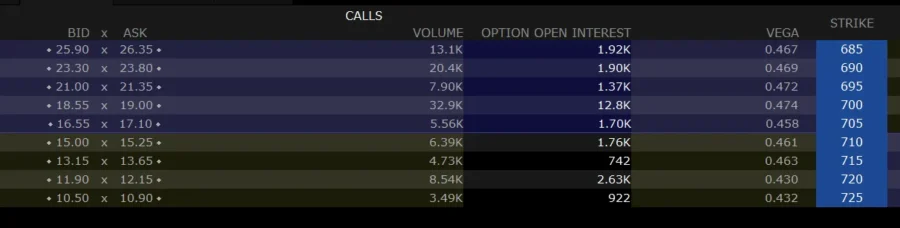
Incorporating vega into your trading strategy involves monitoring market volatility closely and understanding how it can affect your options positions. For instance, in a high-volatility environment, options with a high vega may be more attractive if you anticipate further volatility increases.
In stable markets, options with a lower vega might be preferable, as they are less sensitive to sudden changes in volatility.
To effectively use Vega, stay informed about market conditions and how they might impact the volatility of the assets you’re trading. This includes keeping an eye on economic indicators, news events, and other factors that could influence market sentiment and, by extension, volatility.
Quick Take: What is Vega in options? Vega in options trading is a metric that represents how an option’s price changes in response to a 1% change in the implied volatility of the underlying asset
Understanding Vega Basics and Role in Options Trading
Grasping the concept of vega is fundamental for anyone serious about doing well in options trading. Vega represents the rate at which the price of an option responds to a 1% change in implied volatility. This metric is a key player in the options market, as it sheds light on how volatility swings can influence option prices.
 Understanding the role of vega is a practical necessity for traders. It directly impacts how options are priced concerning shifts in market volatility. By getting a handle on vega, traders can better predict how their option positions might perform and adjust their strategies to either capitalize on or hedge against volatility changes.
Understanding the role of vega is a practical necessity for traders. It directly impacts how options are priced concerning shifts in market volatility. By getting a handle on vega, traders can better predict how their option positions might perform and adjust their strategies to either capitalize on or hedge against volatility changes.
Vega serves as a critical risk assessment tool. It quantifies the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in implied volatility, offering traders a clearer picture of potential risk exposure. In essence, a solid understanding of vega gives traders the ability to fine-tune their approach in response to volatility.
Vega’s Influence on Pricing
Vega plays a significant role in how we assess and predict option pricing through its measurement of an option’s price sensitivity to changes in implied volatility. When implied volatility sees an uptick or downturn, vega shows us how much the price of an option is likely to swing in response. Options with higher vega values are more volatile in terms of pricing, reacting more dramatically to shifts in implied volatility.
On the flip side, options with lower vega values won’t see as much price movement from volatility adjustments.
Understanding the dynamics of vega gives us the knowledge to make better choices when picking options, especially in scenarios where we’re trying to forecast volatility trends. By incorporating vega information into our pricing strategy, we can align our trades more effectively to capitalize on anticipated changes in implied volatility. This approach enhances our profit potential within options trading.
In practical terms, this means keeping a close eye on vega values as part of your trading toolkit. A higher vega might suggest a riskier trade, but with the potential for higher rewards if you’ve accurately anticipated volatility movements. Conversely, a lower vega indicates a more stable option, but with less upside from volatility changes.
Strategies in High Vega Markets
In markets with high vega, traders can profitably use options strategies that take advantage of anticipated shifts in implied volatility
When volatility goes up, options with high Vega increase in value, making them appealing to traders. Traders might look into vertical spreads, a strategy well-suited for high Vega conditions, to capitalize on predicted volatility shifts.
Another tactic is calendar spreads, which involve buying and selling options with differing expiration dates, aiming to profit from Vega variations.
Bull call spreads are also worth considering, as they offer a way to minimize potential losses while still taking advantage of rising stock prices in high Vega conditions.
High Vega Example
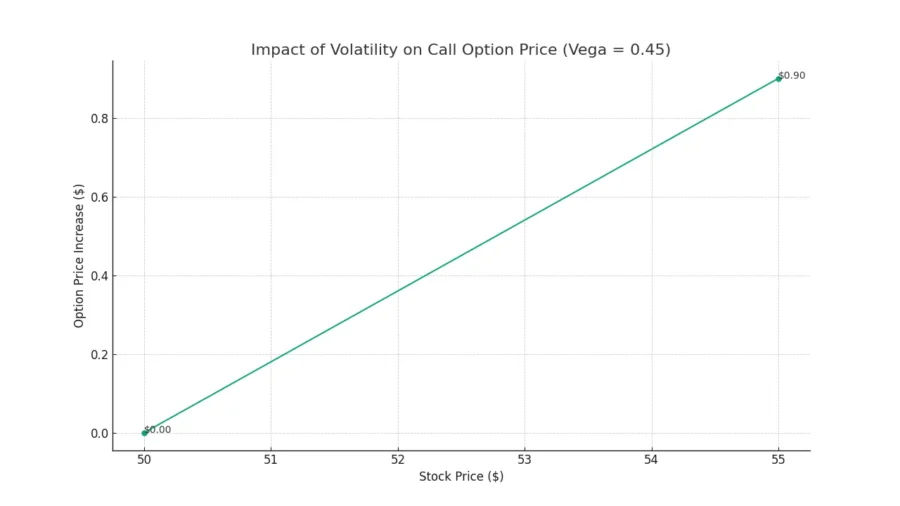
Let’s consider a call option on Stock ABC with a current vega reading of 0.45. If market volatility increases by 1%, the option’s price can be expected to increase by approximately 0.45.
 Now, imagine that the trader anticipates an upcoming event that could potentially lead to a surge in market volatility. In this case, the trader might decide to take advantage of the expected increase in implied volatility by purchasing the call option with a higher vega reading.
Now, imagine that the trader anticipates an upcoming event that could potentially lead to a surge in market volatility. In this case, the trader might decide to take advantage of the expected increase in implied volatility by purchasing the call option with a higher vega reading.
Let’s say the trader purchases the call option when the stock is trading at $50 per share. If the stock’s price subsequently rises to $55 per share and the implied volatility increases by 2%, the vega reading of 0.45 suggests that the option’s price would increase by approximately $0.90 (0.45 x 2).
This price increase would allow the trader to profit from both the underlying stock’s price appreciation and the impact of increased implied volatility, resulting in a potentially higher overall return on investment.
Navigating Low Vega Conditions
When trading in low vega conditions, traders should adjust their options strategies to anticipate reduced implied volatility while still aiming for profitable trading results.
In these scenarios, opting to sell options that exhibit lower Vega values can be a strategic move to capitalize on declining volatility levels. By implementing strategies such as short-call vertical spreads, traders have the opportunity to generate premium income while also establishing a cap on potential losses. The adoption of short-put vertical spreads serves the dual purpose of premium collection and loss mitigation.
Another tactic worth considering is the sale of straddles.
This strategy is particularly advantageous, allowing traders to accumulate premiums while also benefiting from time decay, especially in markets that display minimal price movement and remain within a defined range during periods of low Vega.
Traders need to adjust their strategies to accommodate the reduced price fluctuation resulting from changes in implied volatility characteristic of low Vega environments.
Low Vega Example
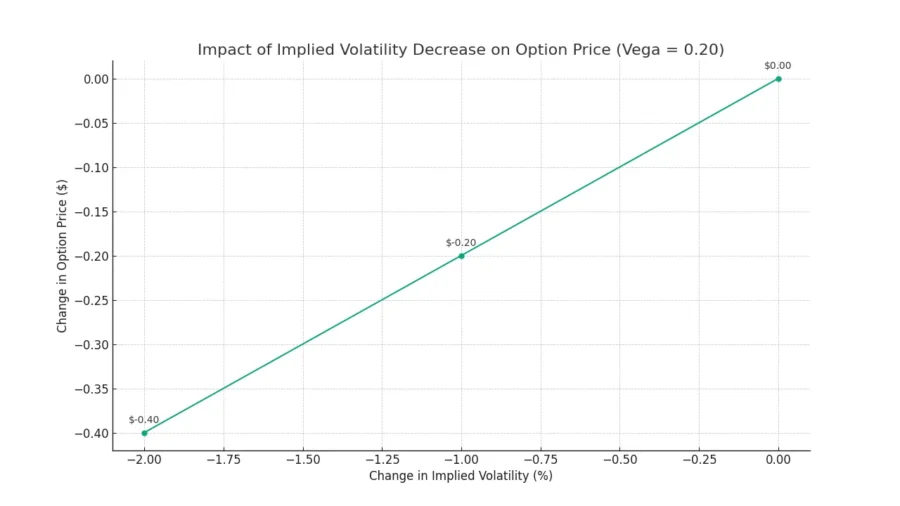
In a scenario where a trader expects decreased volatility, they might consider options with lower vega readings. For example, if the vega reading on a put option for Stock XYZ is 0.20 and the trader predicts a decline in volatility, they might opt for this option over one with a higher vega reading.
 If the stock’s price remains relatively stable and the implied volatility decreases by 1%, the option’s price would be expected to decrease by approximately 0.20.
If the stock’s price remains relatively stable and the implied volatility decreases by 1%, the option’s price would be expected to decrease by approximately 0.20.
Let’s say the trader sells this put option when the stock is trading at $60 per share. If the stock’s price remains flat and the implied volatility decreases by 2%, the vega reading of 0.20 suggests that the option’s price would decrease by approximately $0.40 (0.20 x 2).
By correctly assessing the expected decrease in volatility and choosing an option with a lower vega reading, the trader can potentially benefit from the decrease in option price, leading to a profit on the trade.
Vega Neutral Strategy Essentials
To manage vega neutrality in options trading, use option strategies that offset the effect of implied volatility on option pricing. When implied volatility goes up, option prices usually follow suit, making it necessary to use vega-neutral tactics.
For high vega situations, strategies like vertical spreads, calendar spreads, iron condors, and opting for options with longer expiration dates are effective for managing vega exposure.
On the flip side, in scenarios where vega is low, strategies such as selling straddles, applying the iron butterfly strategy, and using short vertical spreads can be effective in the premium collection while maintaining vega balance.
Vega-neutral strategies require an evaluation of each option’s vega and the use of strategic combinations to mitigate volatility risks. By applying these methods, traders can better handle different vega conditions and aim for vega neutrality in their options trading portfolio.
Vega Neutral Example
Let’s consider a scenario where a trader wants to implement a vega-neutral strategy on a particular stock, ABC. The trader determines that the current implied volatility of options on ABC is relatively high compared to historical levels. To establish a vega-neutral position, the trader can execute the following strategy:
1. Step 1: Buy ABC call options with a higher vega value. These options will benefit from an increase in implied volatility.
2. Step 2: Simultaneously sell ABC put options with a lower vega value to offset the vega exposure from the long call options. These options will be less affected by changes in implied volatility.
By combining these two options positions, the trader creates a vega-neutral strategy. The goal is to profit from other factors, such as underlying price movements or time decay while reducing the sensitivity to changes in volatility.
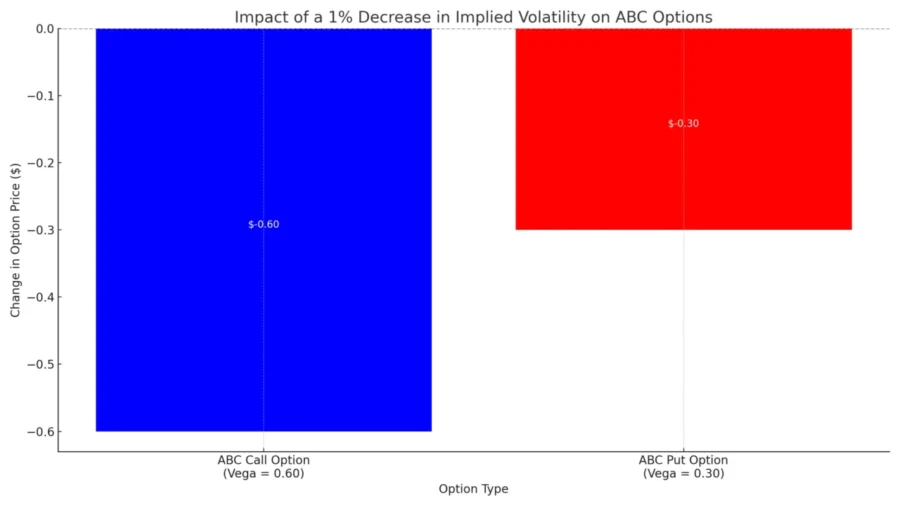 For example,
For example,
- Assume the trader buys call options with a vega of 0.60 and sells put options with a vega of 0.30.
- If the implied volatility of ABC decreases by 1%, the call options’ price might decrease by approximately $0.60, but the put options’ price would decrease by only $0.30.
The offsetting vega values help neutralize the impact of volatility changes on the overall position.
It’s important to note that a vega-neutral strategy doesn’t guarantee profits but rather helps to manage the risk associated with volatility fluctuations. Traders implementing such strategies must closely monitor their positions and make adjustments as needed to maintain vega neutrality as market conditions evolve
Volatility’s Impact on Profits
Let’s get straight to the point: volatility and option prices go hand in hand. For those trading options, understanding this relationship is key to making better trades and protecting your capital.
Here’s the rundown: Vega measures an option’s price sensitivity to changes in implied volatility. If volatility goes up, so do option prices, which can be good news for those holding long option positions. On the flip side, if volatility drops, option prices might decrease, which isn’t ideal if you’re looking to maximize profits.
How can you play this to your advantage?
By using strategies that depend on Vega to anticipate shifts in implied volatility, you can potentially beef up your profits. This approach isn’t just about profits; it’s also about smart risk management. By keeping an eye on volatility and adjusting your strategies accordingly, you can mitigate losses which is vital for long-term success in trading.
Managing Risk With Vega
When Vega is high, certain strategies become more appealing. These include vertical spreads, calendar spreads, iron condors, and straddles. These tactics are designed to navigate through unpredictable market movements by limiting potential losses while aiming for positive financial results.
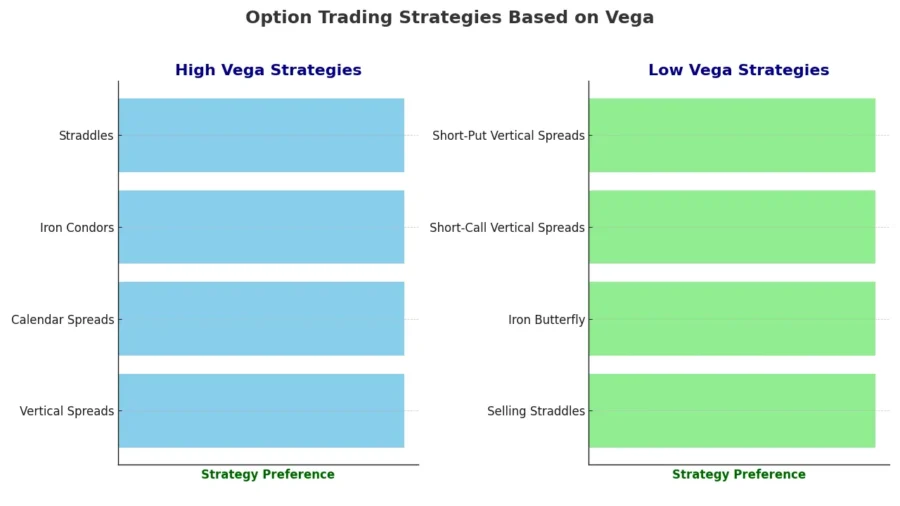 On the flip side, when Vega is low, different approaches are advisable. Selling straddles, employing iron butterfly strategies, and opting for short-call and put vertical spreads can lead to beneficial outcomes. These strategies are generally less sensitive to sharp swings in volatility, making them suitable for more stable market conditions.
On the flip side, when Vega is low, different approaches are advisable. Selling straddles, employing iron butterfly strategies, and opting for short-call and put vertical spreads can lead to beneficial outcomes. These strategies are generally less sensitive to sharp swings in volatility, making them suitable for more stable market conditions.
Besides strategy selection based on Vega, risk management in options trading also involves diversification, setting stop-loss orders, and exercising patience.
- Diversification spreads risk across various assets or strategies, reducing the impact of any single investment’s poor performance
- Stop-loss orders help limit losses by automatically selling assets at a predetermined price
- Patience is necessary to weather the ups and downs of the market without making hasty decisions that could lead to significant losses
Understanding Vega and its implications on options pricing is fundamental for constructing effective hedging strategies. A hedging strategy aims to offset potential losses in one position with gains in another.
Conclusion
To effectively maximize your returns in options trading, a deep understanding of vega volatility is worthwhile. Vega plays a pivotal role in option pricing by measuring an option’s sensitivity to changes in the underlying asset’s volatility. By utilizing Vega to your advantage, you stand to significantly enhance your profit margins.
