- October 19, 2024
- Posted by: CoachShane
- Categories: Day Trading, Swing Trading, Trading Article

When you’re considering your approach to trading, you’ll often find yourself at a crossroads: should you opt for short-term or long-term strategies? Each path offers unique advantages and challenges that can significantly impact your financial journey.
Short-term trading might appeal to your desire for quick gains and active market participation, while long-term trading could align with your patience and belief in steady growth.
As you weigh these options, you’ll need to consider factors like your risk tolerance, time commitment, and overall investment goals. The choice you make will shape not only your trading style but also your potential for success in the markets.
What are Zero-DTE Options? => Download “Zero-DTE Options Trading Secrets” right here
TLDR
- Short-term trading involves holding positions for minutes to days, while long-term trading spans months to years.
- Short-term traders rely heavily on technical analysis, whereas long-term traders focus more on fundamental analysis.
- Short-term trading offers quick profit realization but incurs higher transaction costs and stress levels.
- Long-term trading benefits from compounding returns and lower costs but is more vulnerable to economic changes.
- Trading frequency depends on individual goals, risk tolerance, and available time for market analysis and monitoring.
Understanding Short-Term Trading
Short-term trading is a fast-paced approach to the financial markets, typically involving positions held for minutes, hours, or days.
You’ll need to be comfortable with rapid price movements and be able to spot short-term trends as they develop. Setting clear profit targets and maintaining discipline is important for success in short-term trading, especially when starting with a small account.
As a short-term trader, you’ll rely heavily on technical analysis. This involves studying charts, patterns, and indicators to predict future price movements.
You’ll often find yourself glued to your screen, watching for sudden shifts in market sentiment.
Day trading is a popular form of short-term trading. It involves opening and closing positions within a single trading day.
You’ll need to be disciplined and have a solid risk management strategy in place.
One advantage of short-term trading is that you can potentially profit from both rising and falling price action on the same day. However, it’s important to remember that this approach can be stressful and time-consuming.
You’ll need to be prepared for frequent trades and the emotional rollercoaster that comes with rapid gains and losses.
Advantages of Short-Term Trading
Short-term trading offers several advantages that you might find attractive.
You’ll have the opportunity to realize profits quickly, often within days or even hours. This approach also provides you with greater flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions and reduces your overall exposure to prolonged market risks.
Day trading strategies often involve frequent buying and selling within short time frames, allowing traders to capitalize on small price movements.
Quick Profit Realization
Short-term trading strategies offer quick profits and a significant advantage over longer-term trading. When you adopt this trading style, you can capitalize on market fluctuations within a shorter time frame. This approach allows you to see the results of your trades more rapidly, which can be both exciting and motivating.
Quick profits in short-term trading offer several benefits:
- Faster capital turnover: You can reinvest your gains more frequently.
- Reduced exposure to long-term market risks: Your money isn’t tied up for extended periods.
- Opportunity to compound gains: More trades mean more chances to grow your investment.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Another key advantage of short-term trading is its inherent flexibility and adaptability. As a short-term trader, you’ll find it easier to adjust your trading strategy based on changing market conditions. You can quickly shift your focus from one asset to another or modify your approach as new information becomes available.
This flexibility allows you to tailor your time horizon to your risk tolerance and trading experience. If you’re new to trading, you can start with smaller positions and shorter time frames, gradually increasing your exposure as you gain confidence. You’ll also be able to take advantage of short-lived market inefficiencies and capitalize on brief price movements.
Short-term trading enables you to adapt to various market environments. During volatile periods, you can reduce your position sizes or switch to more stable assets. In calmer markets, you might explore alternative strategies or focus on specific sectors.
This adaptability helps you maintain consistent performance across different market conditions, potentially leading to more stable returns over time. Remember, the key to success in short-term trading is staying nimble and responsive to market changes.
Lower Exposure to Market Risk
One significant advantage of short-term trading is the reduced exposure to market risk. When you only take short-term trades, you’re less likely to be affected by long-term market trends or economic shifts. This lower level of risk exposure can be particularly appealing if you’re new to trading or prefer a more cautious approach.
Short-term trading offers several benefits in terms of risk management:
- Quick exits: You can quickly close positions if the market moves against you, limiting potential losses.
- Smaller price movements: Short-term trades often capitalize on smaller price fluctuations, reducing the impact of major market swings.
- Frequent portfolio rebalancing: You can adjust your holdings more often, allowing for better risk diversification.
Compared to long-term trades, short-term strategies typically involve less time exposed to market volatility. This means you’re less likely to experience significant drawdowns during extended bear markets.
Disadvantages of Short-Term Trading
While short-term trading can be exciting, it comes with drawbacks you should consider.
You’ll face higher transaction costs due to frequent trades, which can eat into your profits. The fast-paced nature of short-term trading often leads to increased stress and demands more of your time and attention.
Day trading, in particular, requires constant monitoring and quick decision-making, as profit targets are smaller compared to longer time frames.
Additionally, you’ll need to handle the challenges of market volatility, which can quickly turn profitable positions into losses.
Higher Transaction Costs
The constant clicking of the “buy” and “sell” buttons comes at a price for short-term traders. When you engage in frequent trading, especially day trading strategies, you’ll face higher transaction costs that can significantly impact your trading profitability.
These costs add up quickly, eating into your potential gains and making it harder to turn a profit.
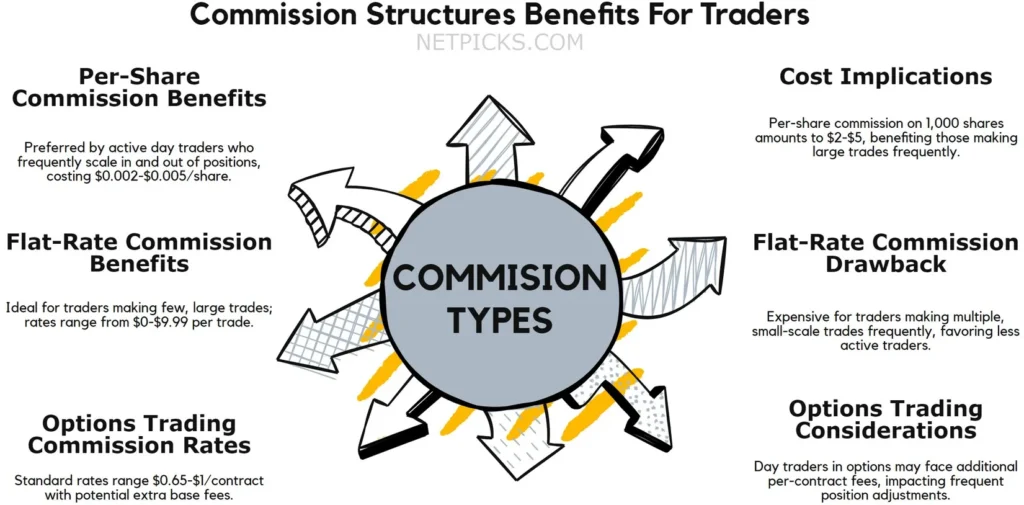
Here’s why transaction costs are a major concern for short-term trading:
- Commissions: You’ll pay a fee for each trade, which multiplies with increased trading frequency.
- Spreads: The difference between bid and ask prices can be substantial, especially in volatile markets.
- Slippage: Rapid price movements can result in executions at less favorable prices than expected.
These costs can quickly erode your profits, especially if you’re making numerous trades daily.
While some brokers offer lower fees for high-volume traders, the cumulative effect of these costs can still be significant.
To combat this issue, you’ll need to ensure that your short-term trading strategies generate enough profit to overcome these expenses.
You need to factor in these costs when evaluating your trading performance and deciding whether short-term trading is right for you.
Increased Stress and Time Commitment
As a short-term trader, you’ll find yourself constantly glued to the charts and monitoring intraday volatility. This intense focus on shorter trading time frames can lead to increased stress and a significant time commitment.
You’ll need to be prepared for long hours in front of your screens, often starting before the market opens and extending well after it closes. The fast-paced nature of short-term trading demands quick decision-making and constant alertness, which can be mentally exhausting. Here’s a breakdown of how your time might be spent:
| Activity | Hours per Day | Stress Level |
|---|---|---|
| Market Analysis | 3-4 | High |
| Active Trading | 6-8 | Very High |
| Research | 2-3 | Moderate |
This intense schedule can impact your personal life and overall well-being. You must assess whether this level of commitment aligns with your trading goals and lifestyle.
Remember, successful short-term trading requires not just skill, but also the ability to manage stress and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
Challenges of Market Volatility
You’ll encounter daily volatility that can make or break your trading strategy. Short-term market fluctuations often don’t align with broader market trends, making it difficult to predict outcomes accurately.
To tackle these challenges, you’ll need to:
- Develop a solid risk management plan
- Stay informed about market news and events
- Use technical analysis tools to identify potential entry and exit points
Short-term volatility can be both a blessing and a curse. While it creates opportunities for quick profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses.
You’ll need to be prepared for rapid short-term price movements that can occur within minutes or even seconds. This requires constant vigilance and quick decision-making skills.
Understanding Long-Term Trading
Long-term trading involves holding positions for extended periods, typically months or even years. It’s a strategy that focuses on the big picture in financial markets, relying heavily on fundamental analysis.
When you’re a long-term trader, you’ll need patience and a broader investment horizon. You’ll be looking at factors like company financials, industry trends, and economic indicators to make decisions.
Here’s a comparison of long-term trading characteristics:
| Aspect | Long-Term Trading |
|---|---|
| Time Frame | Months to Years |
| Analysis | Fundamental |
| Risk | Generally Lower |
| Emotional Impact | Less Stressful |
| Capital Required | Often Higher |
Long-term trading can be less stressful than short-term strategies because you’re not constantly watching market fluctuations. You’ll need to develop a deep understanding of the assets you’re investing in and the factors that influence their value over time. This approach often requires more capital, as you’ll be tying up your funds for extended periods.
However, it can also lead to significant gains if you’ve chosen well. Remember, long-term trading isn’t about fast daily profits; it’s about building wealth over time.
Advantages of Long-Term Trading
When you choose long-term trading, you’ll enjoy several key benefits.
You’ll make fewer trades, cutting down on transaction costs and the time you spend actively managing your portfolio. Long-term trading also allows for less frequent market pulse checks, similar to swing trading, which can free up time for other activities while remaining market active.
Your investments have more time to grow through compounding returns, potentially leading to larger gains over extended periods. Long-term trading can also be less stressful, as you’re not constantly reacting to short-term market fluctuations, which can help maintain your emotional stability.
Reduced Transaction Frequency
One of the key advantages of long-term trading is the reduced frequency of transactions. When you engage in long-term trading strategies, you’re not constantly buying and selling assets like you’d with short-term strategies.
This lower transaction frequency offers several benefits:
- Lower costs: You’ll pay fewer commission fees and spread costs over time.
- Less stress: You won’t need to monitor the market as closely or make quick decisions.
- More time for analysis: You can thoroughly research potential trading opportunities.
By holding positions for an extended period, you’ll naturally have fewer transactions. This approach allows you to focus on the bigger picture and overall market trends rather than day-to-day fluctuations.
You’ll spend less time executing trades and more time analyzing market conditions and potential investments.
Reduced transaction frequency also means you’re less likely to make impulsive decisions based on short-term market movements. This can help you stick to your trading plan and avoid emotional reactions to temporary market volatility.
Compounding Returns Over Time
Have you ever heard the phrase “compound interest is the eighth wonder of the world”? This concept applies to long-term trading as well.
When you adopt a long-term investment strategy, you’re giving your investment capital more time to grow through compounding returns. This means your profits can generate additional profits over time, potentially accelerating your progress toward your investment goals.
Here’s a simple example of how compounding works:
| Year | Initial Investment | Annual Return | End-of-Year Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $10,000 | 10% | $11,000 |
| 2 | $11,000 | 10% | $12,100 |
| 3 | $12,100 | 10% | $13,310 |
| 4 | $13,310 | 10% | $14,641 |
As you can see, your investment grows faster over time due to compounding. This effect becomes even more powerful with longer time frames. By focusing on long-term trading, you’re giving your investments more time to benefit from this compounding effect. It’s a patient approach that can lead to significant wealth accumulation over the years, making it an attractive strategy for many investors.
Better for Emotional Stability
While the financial benefits of long-term trading are persuasive, there’s another significant advantage: emotional stability. When you adopt a long-term strategy, you’re less likely to be swayed by short-term market noise. This approach can lead to more rational and informed trading decisions, as you’re not constantly reacting to every market fluctuation.
A long-term perspective offers several emotional benefits:
- Reduced stress: You’re not glued to your screen watching every tick of the market.
- Improved focus: You can concentrate on broader market trends and fundamentals.
- Better risk management: You’re less likely to make impulsive decisions based on fear or greed.
Disadvantages of Long-Term Trading
While long-term trading can offer stability, it’s not without its drawbacks.
You’ll likely see smaller immediate profits compared to short-term strategies, and your investments are more vulnerable to major economic shifts over time.
Swing trading strategies can provide a balance between short-term gains and long-term stability, offering more flexibility in capturing market movements.
Additionally, you’ll need to consider the tax implications of holding onto assets for extended periods, as long-term capital gains may be treated differently than short-term trades.
Potential for Lower Immediate Profits
Long-term trading often comes with a trade-off: the potential for lower immediate profits.
Unlike short-term investments that focus on quick trades and daily price fluctuations, long-term strategies prioritize gradual growth over time. This approach means you won’t see the same rapid gains that profitable trades in shorter timeframes might yield.
While your share price may increase substantially over the years, you’ll miss out on the excitement of frequent wins (not a bad thing – trading should not be emotional).
Here are three reasons why long-term trading might result in lower immediate profits:
- Slower capital turnover
- Missed short-term opportunities
- Extended exposure to market volatility
When you’re holding onto stocks for extended periods, your money isn’t working as hard in the short term (minus dividend investing). You might watch others capitalize on market trends while your investments slowly appreciate. This can be frustrating, especially when you see others making quick gains.
However, it’s important to remember that long-term trading isn’t about immediate gratification. It’s about building wealth over time, reducing the stress of constant market monitoring, and potentially benefiting from compounding returns.
Higher Sensitivity to Economic Changes
Despite its potential benefits, long-term trading exposes investors to greater economic risks over time. When you hold positions for extended periods, you’re more vulnerable to macroeconomic trends and market cycles that can significantly impact your financial instruments.
Unlike short-term trading, where you can quickly react to short-term fluctuations, long-term strategies require you to weather various economic storms.
Economic indicators play a role in shaping market sentiment and direction. As a long-term trader, you’ll need to stay informed about these factors:
| Economic Factor | Impact on Markets | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Affects borrowing | Fed rate hikes |
| Inflation | Erodes value | Rising CPI |
| GDP Growth | Drives sentiment | Recession fears |
These factors can cause substantial shifts in asset values over time. While short-term traders might capitalize on quick moves, you’ll need to be prepared for prolonged periods of uncertainty. This higher sensitivity to economic changes means you’ll have to constantly reassess your strategy and be ready to adjust your positions if market conditions shift dramatically.
Tax Implications on Gains
Tax considerations add another layer of complexity to long-term trading strategies. When you’re holding investments for extended periods, you’ll need to keep track of how your gains are taxed. Long-term capital gains often benefit from lower tax rates compared to short-term gains, which are taxed as ordinary income.
However, this doesn’t always mean long-term trading is the better choice for your tax situation.
Here are three key points to consider:
- Your overall tax bracket can impact the benefits of long-term vs. short-term trading.
- Long-term strategies may limit your ability to take advantage of short-term movements.
- Tax implications shouldn’t be the sole factor in your investment decisions.
It’s important to understand how both short-term and long-term trading strategies can affect your tax bill. While long-term gains might offer tax advantages, they could also tie up your capital for extended periods.
On the other hand, short-term trading allows for more flexibility but may result in higher taxes. Always consult with a tax professional to understand how your trading activities align with your overall financial goals and tax situation.
Key Differences Between Short-Term and Long-Term Trading
When comparing short-term and long-term trading, you’ll find significant differences in time commitment, risk management, and profit goals.
Short-term traders need to dedicate more time to market analysis and quick decision-making, while long-term traders can take a more relaxed approach.
You’ll also notice that short-term trading often involves higher risk and potential for quick gains, whereas long-term trading typically aims for steady growth with lower overall risk.
Time Commitment and Analysis
Time investment and analytical depth mark significant distinctions between short-term and long-term trading approaches.
As a day trader, you’ll spend more hours actively monitoring short-term market movements and making quick decisions. You’ll rely heavily on technical analysis indicators to spot immediate opportunities.
In contrast, long-term traders focus on broader market trends and fundamental analysis, requiring less daily time commitment but more patience.
The analytical processes for these trading types differ significantly:
- Short-term traders analyze minute-by-minute charts and news.
- Long-term traders study quarterly reports and macroeconomic trends.
- Day traders use multiple technical indicators, while long-term traders prioritize fundamental analysis.
Your time commitment will vary based on your chosen strategy.
Short-term trading demands constant attention during market hours, often requiring you to make split-second decisions. You’ll need to stay glued to your screens, analyzing rapid price movements.
Long-term trading, however, allows for a more relaxed approach. You’ll spend less time on daily analysis but must dedicate effort to thorough research and periodic portfolio reviews.
Both strategies require discipline, but the intensity and frequency of your engagement will differ significantly.
Risk Tolerance and Management
Risk tolerance and management strategies differ significantly between short-term and long-term trading approaches. In short-term trading, you’ll need to be comfortable with higher levels of risk and frequent changes in your risk positions.
You’ll face more “operational risk” due to the need for quick decision-making and execution.
On the other hand, long-term trading allows for a more relaxed approach to risk management, with less frequent adjustments to your positions.
Here’s a comparison of risk factors in short-term and long-term trading:
| Risk Factor | Short-Term Trading | Long-Term Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Volatility | High exposure | Lower exposure |
| Stop-loss | Tighter | Wider |
| Margin | Often higher | Usually lower |
| Overnight risk | Higher | Lower |
| Trading capital | Smaller amounts | Larger amounts |
When short-term trading, you’ll need to be prepared for the risk of overnight price gaps and sudden market movements. You’ll typically use a smaller portion of your trading capital for each trade.
Long-term trading, however, allows you to weather short-term volatility and use a larger portion of your capital for each position. Ultimately, your choice between these approaches should align with your personal risk tolerance and financial goals.
Profit Potential and Goals
Regarding profit potential and goals, short-term and long-term trading approaches offer distinct opportunities and challenges. Your choice between these types of trading will depend on your financial objectives, risk tolerance, and available time for trading.
Short-term trading aims for quick profits from small price movements, while long-term trading seeks larger gains over extended periods.
When considering profit potential and goals, keep these key points in mind:
- Short-term trading often yields smaller, more frequent profits, while long-term trading targets larger gains but requires patience.
- Long-term strategies typically involve lower transaction costs due to fewer trades.
- Short-term trading demands more time and attention, as you’ll need to monitor markets closely and exit trades quickly.
Your trading profit potential depends on your strategy, market conditions, and skill level. Short-term traders might see daily or weekly results, while long-term investors may wait months or years for significant returns.
Be sure to align your trading approach with your personal goals and lifestyle. Remember, both strategies can be profitable if executed properly, but they require different skills and time commitments.
Trading Frequency Considerations
When it comes to trading frequency, you’ll need to consider how often you should trade, how your trading style affects this, and what pace suits you best.
Your trading frequency can significantly impact your results, so find the right balance for your strategy and lifestyle. Pattern Day Trader rules may affect your trading frequency if you’re operating with a margin account and less than $25,000 balance.
It’s important to be aware of these regulations when planning your trading schedule. Take time to assess your goals, available resources, and risk tolerance to determine the ideal trading frequency for your situation.
How Often Should You Trade?
Determining the ideal trading frequency is an aspect of developing your trading strategy.
Your trading days and how often you trade depend on several factors, including your type of trading strategy, available time, and financial goals. If you’re into intraday trading, you might find yourself active daily, while long-term investing requires less frequent trades.
To help you decide how often you should trade, consider these key points:
- Your trading style: Day traders may execute multiple trades daily, while swing traders might hold positions for days or weeks.
- Available time: Assess how much time you can dedicate to market analysis and trade execution.
- Risk tolerance: More frequent trading often involves higher risk, so align your trading frequency with your comfort level.
Impact of Trading Style on Frequency
Your trading style plays a role in determining how often you’ll execute trades. Different types of trading are associated with varying periods, which directly impact your trading frequency.
- Day trading: you’ll likely be making multiple trades each day, sometimes even within minutes.
- Swing trading: might see you holding positions for a few days to weeks, resulting in less frequent trades.
- Long-term approach: position trading or buy-and-hold strategies, you’ll trade much less often, perhaps only a few times a year.
Your choice between short-term or long-term trading styles will depend on various factors, including your risk tolerance, available time, and market analysis skills.
It’s important to understand that more frequent trading doesn’t necessarily mean better results. Each style has its pros and cons.
Short-term trading can offer quick profits but requires constant market monitoring and can be stressful. Long-term trading, while less time-intensive, requires patience and a strong understanding of fundamental analysis.
Choose a style that aligns with your personality and lifestyle for the best results.
Identifying the Right Pace for You
Finding the right trading pace involves several key considerations. As a beginner trader, you’ll need to assess your personal preferences, financial goals, and available time.
Short-term trading requires more frequent monitoring and quick decision-making, while long-term trading allows for a more relaxed approach. Your trading portfolio’s size and diversity will also influence your ideal pace.
To identify the right pace for you, consider these factors:
- Time commitment: How much time can you dedicate to market analysis and trade execution?
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable with the higher volatility of short-term trading or prefer the stability of long-term investments?
- Emotional resilience: Can you handle the stress of frequent trading, or do you need a slower pace to maintain composure?
Your Questions Answered
How Do Economic Cycles Impact Short-Term Versus Long-Term Trading Strategies?
Economic cycles affect your trading strategies differently. In the short term, you’ll need to adapt quickly to market fluctuations. For long-term strategies, you can ride out temporary ups and downs, focusing on broader economic trends.
What Role Does Market Volatility Play in Choosing Between Timeframes?
Market volatility greatly influences your timeframe choice. When volatility’s high, you’ll often prefer shorter timeframes to capture quick moves. In calmer markets, you might opt for longer timeframes to benefit from sustained trends and avoid noise.
Can Traders Successfully Combine Both Short-Term and Long-Term Approaches?
You can combine short-term and long-term approaches. It’s called a multi-timeframe strategy. You’ll use longer timeframes for overall trends and shorter ones for entry and exit points. It’s a powerful way to trade. You can even day trade in the instruments you are holding long term.
How Do Commission Costs Differ Between Short-Term and Long-Term Trading?
You’ll typically pay higher commission costs with short-term trading due to more frequent transactions. Long-term trading involves fewer trades, resulting in lower overall fees. Consider these costs when choosing your strategy to maximize profits.
Are Certain Asset Classes Better Suited for Short-Term or Long-Term Trading?
You’ll find that some assets are better for short-term trading, like volatile stocks and forex. For long-term trading, consider stable blue-chip stocks, bonds, and ETFs. Your strategy should match the asset’s characteristics and market behavior.
Conclusion
Each has its pros and cons, so you need to choose what fits your lifestyle and goals. Short-term trading offers quick profits but requires more time and stress. Long-term trading provides stability but slower gains. Consider your risk tolerance, time availability, and market knowledge when deciding. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. The best strategy is the one that aligns with your circumstances and financial objectives.
