- September 6, 2024
- Posted by: CoachShane
- Categories: Trading Article, Trading Indicators

As a trader, you’ve likely seen the MACD histogram when you use the MACD lines. It’s a powerful indicator that can reveal important information about market momentum and potential trend reversals.
Understanding the subtleties of the MACD histogram can significantly improve your trading decisions, helping you spot opportunities and avoid pitfalls that others might miss. From interpreting bar heights to recognizing divergences, there’s more to this tool than pretty colors.
Are you an options trader? Did you know 53% of options trades are now short term… or Zero-DTE options? If you want to profit from this hot new market, download my Free “Zero-DTE Options Trading Secrets” report NOW!
Breaking Down the MACD Histogram
The MACD Histogram serves as a powerful tool for traders. This oscillator, derived from the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator, provides valuable observations into price momentum and potential trend reversals.
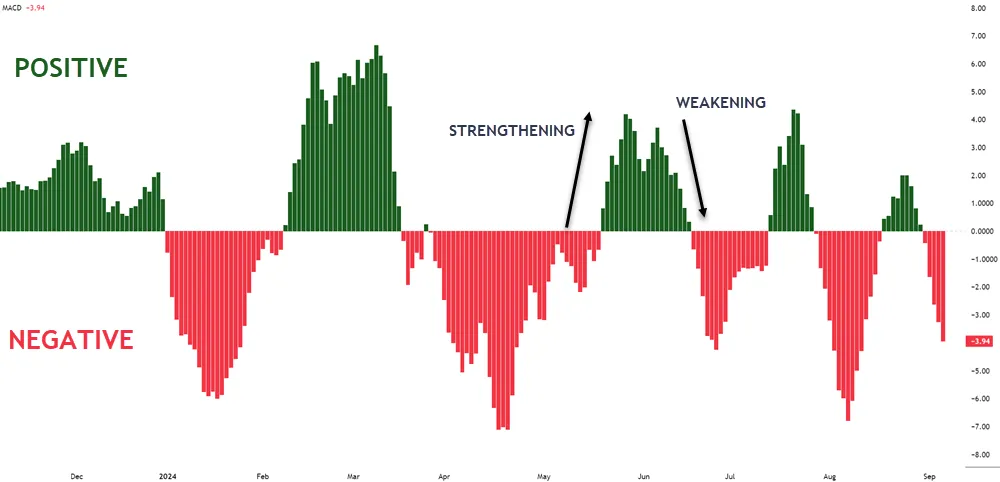
To understand the MACD Histogram effectively, you’ll need to focus on two key aspects: bar height and direction.
| MACD Indicator | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Positive Histogram | Bullish momentum |
| Negative Histogram | Bearish momentum |
| Increasing Bar Height | Strengthening trend |
| Decreasing Bar Height | Weakening trend |
Histogram Trends

| Trend Indicator | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Divergence | Price and histogram move in opposite directions, signaling a potential trend reversal |
| Zero-line Crossover | Indicates a shift in momentum from bullish to bearish or vice versa |
As you analyze the MACD Histogram, pay attention to these patterns and their implications for price action (look for the price confirming the indicator).
Remember, the histogram’s primary function is to visualize the difference between the MACD line and its signal line. By observing changes in bar height and direction, you can gain a better understanding of market momentum and make better trading decisions.
Always use the MACD Histogram alongside other technical indicators for a comprehensive analysis.
Bullish and Bearish Signals
The MACD Histogram provides clear bullish and bearish signals that can guide your trading decisions. When the histogram bars are above the zero line and increasing in height, it indicates bullish momentum.
Bars below the zero line and growing deeper suggest bearish momentum. Pay attention to crossovers: when the histogram crosses above the zero line, it’s a bullish signal, while crossing below is bearish.
| Signal Strength Indicator | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Bar Height | Taller bars indicate stronger signals |
| Slope | Steeper slopes suggest more vigorous momentum |
| Duration | Longer-lasting patterns are more reliable |
Confirming Signals
| Confirming Signal | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Trading Volume | Higher volume supports signal reliability |
| Price Action | Look for corresponding candlestick patterns |
| Market Trends | Align signals with broader market direction |
To use confirming signals for validating MACD Histogram signals, follow these guidelines:

1. Trading Volume
- Importance: Higher trading volume indicates stronger market participation and can validate the reliability of MACD signals.
- How To Use: When you see a MACD signal (like a bullish crossover), check if the trading volume is above average. A significant increase in volume during the signal can confirm its strength. For instance, if a bullish MACD signal occurs alongside a volume spike, it suggests strong buying interest, reinforcing the signal’s validity.
2. Price Action
- Importance: Price action refers to the movement of a security’s price and can provide context to MACD signals.
- How To Use: Look for corresponding candlestick patterns that align with the MACD signal. For example, if the MACD indicates a bullish trend, check for bullish candlestick patterns like engulfing or hammer formations. These patterns can indicate that buyers are gaining control, thus confirming the MACD signal.
3. Market Trends
- Importance: Aligning MACD signals with broader market trends enhances their reliability.
- How To Use: Assess the overall market direction (bullish or bearish) before acting on MACD signals. If the MACD shows a bullish signal but the broader market is in a downtrend, it may be less reliable. If both the MACD and the market trend are bullish, it strengthens the case for entering a trade.
By adding in these confirming signals—trading volume, price action, and market trends—you can improve your trading strategy by making decisions based on other confirmations.
Divergence Analysis Techniques
Divergence analysis techniques come into play when the MACD Histogram‘s behavior doesn’t align with price action. These divergence patterns often signal potential momentum shifts and trend reversals, providing valuable observations for traders.
You’ll see two primary types: bullish and bearish divergences.
Bullish divergences occur when prices make lower lows, but the MACD Histogram shows higher lows. This suggests decreasing downward momentum and a possible trend reversal.

Bearish divergences happen when prices reach higher highs, while the MACD Histogram displays lower highs, indicating weakening upward momentum.
To use divergence analysis:
- Confirm signals with other indicators or chart patterns
- Consider multiple timeframes for a comprehensive view
- Incorporate volume analysis to validate momentum shifts
- Implement proper risk management strategies
Histogram-Based Trading Strategies
Building on the understanding gained from divergence analysis, traders can develop specific strategies centered around the MACD Histogram‘s movements. As one of the most versatile momentum indicators, the MACD Histogram offers valuable perspectives for trend confirmation and entry timing.
Histogram-Based Trading Strategies:
| Strategy/Indicator | Action/Description |
|---|---|
| Zero-Line Crossover | Enter long positions when the histogram crosses above zero |
| Enter short positions when it crosses below zero | |
| Use this as a trend confirmation tool | |
| Signal Strength Assessment | Evaluate histogram bar height to gauge momentum |
| Larger bars indicate stronger signals, while smaller bars suggest weakening trends | |
| Divergence-Based Entries | Identify divergences between price action and histogram |
| Enter trades when divergences resolve, confirming trend reversals | |
| Exit Strategies | Use histogram reversals as exit signals |
| Implement trailing stops based on histogram movements | |
| Risk Management | Set stop-losses at recent swing highs/lows |
| Adjust position sizes based on histogram volatility |
Avoiding Common Interpretation Errors
Despite its usefulness, the MACD Histogram can lead to misinterpretation if you’re not careful. To avoid common issues that traders make, you must understand the subtleties of interpretation and recognize that the histogram isn’t perfect.
Avoiding Common Interpretation Errors:
- Overreliance on Divergence:
While divergence can be a powerful signal, don’t assume it always predicts trend reversals. Market conditions and other indicators should corroborate your analysis. - Ignoring Time Frames:
The histogram’s effectiveness varies across different time frames. What appears significant on a daily chart may be insignificant on a weekly one. Always consider multiple time frames for a comprehensive view. - Misinterpreting Zero Line Crosses:
Zero-line crosses don’t necessarily indicate immediate trade entries or exits. They’re often lagging signals and should be used in conjunction with other technical factors. - Neglecting Volume:
The histogram doesn’t account for volume. High-volume moves are typically more significant than low-volume ones, so incorporate volume analysis into your decision-making process. - Overlooking Broader Market Context:
Don’t analyze the MACD Histogram in isolation. Consider macroeconomic factors, sector trends, and company-specific news that may impact price movements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the MACD Histogram Differ From the Traditional MACD Indicator?
Unlike traditional MACD signals, the histogram visualizes the difference between MACD and signal lines. You’ll find it easier to spot trend strength and potential reversals. Histogram analysis offers a more immediate, visual representation of price momentum.
Can the MACD Histogram Be Used Effectively in Different Market Conditions?
You can effectively use the MACD histogram in various market conditions. It’s versatile for identifying market trends and enhancing trading strategies. Use it for signal confirmation, but don’t forget to incorporate other tools for comprehensive risk management.
What Timeframes Work Best When Analyzing the MACD Histogram?
You’ll find the MACD histogram useful across various timeframes. For short-term strategies, focus on daily or hourly charts. To analyze long-term trends, consider weekly or monthly timeframes. Adapt your approach based on your trading goals.
How Does Volume Affect the Reliability of MACD Histogram Signals?
You’ll find that volume trends significantly affect MACD histogram signals. Higher volume can provide stronger signal confirmation. When you see increasing volume alongside a histogram signal, you’re more likely to have a reliable trading opportunity.
Are There Any Specific Industries Where the MACD Histogram Is Particularly Effective?
You’ll find the MACD histogram particularly effective in healthcare stocks and technology sectors (due to volatility). It’s also useful for energy markets and consumer goods. However, its effectiveness can vary, so you should always combine it with other indicators.
Conclusion
You’ll find the MACD histogram to be a great tool in your trading toolkit. By mastering its interpretation, you’ll give yourself with a powerful means of gauging market momentum and potential reversals. Remember, while the histogram offers valuable information, it’s most effective when used in with other technical indicators.
